Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of arthritis. Also known as degenerative joint disease.
Genicular artery embolization (GAE)
What is Knee Osteoarthritis(OA)?
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of arthritis. Also known as degenerative joint disease.
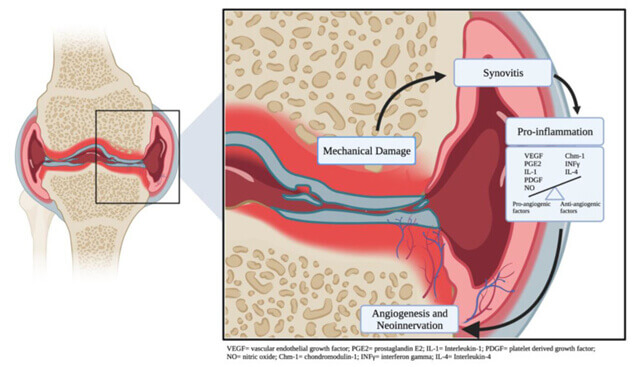
Old school belief: Knee OA occurs as “wear and tear” arthritis. However, recent scientific research suggests this is a direct result of synovial inflammation(increased blood flow) releasing a chemical in the knee joint leads to further destruction of the joint. The inflammation likely contributes to the degeneration of the joint.
With OA, the cartilage within a joint begins to break down and the underlying bone begins to change. Resulting in pain symptoms.
How is Knee Osteoarthritis(OA) diagnosed?
A doctor diagnoses OA through a review of symptoms, physical examination, X-rays, and lab tests.
What are the symptoms of Knee Osteoarthritis(OA)?
Most common symptoms are debilitating knee pain and stiffness. Symptomatic Knee OA changes usually develop slowly and get worse over time. OA can also cause swelling and gait changes, and decrease morale and quality of life due to reduced function and disability; some people are no longer able to do daily tasks or work.
What are the demographics and risk factors for Knee Osteoarthritis(OA)?
Numbers are eye-popping!!
- Knee OA will affect 50% of Americans during their lifetime.
- MORE THAN 1/3 OF Americans older than 60 years of age will experience chronic pain from knee OA.
Risk factors are as follows:
- Joint injury or overuse—Injury or overuse, such as knee bending and repetitive stress on a joint, can damage a joint and increase the risk of OA in that joint.
- Age—The risk of developing OA increases with age.
- Gender—Women are more likely to develop OA than men, especially after age 50.
- Obesity—Extra weight puts more stress on joints, particularly weight-bearing joints like the hips and knees. This stress increases the risk of OA in that joint. Obesity may also have metabolic effects that increase the risk of OA.
- Genetics—People who have family members with OA are more likely to develop OA. People who have hand OA are more likely to develop knee OA.
- Race— Some Asian populations have a lower risk for OA.
What is a knee embolization or Genicular artery embolization (GAE)?
This is a cutting-edge, innovative procedure directed towards decreasing inflammation to the knee joint via reducing the blood supply to the lining of the knee which in turn relieves aching and stiffness from knee osteoarthritis.
Is Genicular artery embolization (GAE) a minimally invasive procedure?
Yes. Unlike an invasive knee replacement surgery, Dr. Nanavati, an experienced Interventional Radiologist, performs an image-guided outpatient procedure delaying or avoiding knee replacement surgery while pausing knee Osteoarthritis, which controls symptoms and significantly improves and restores quality of life. Isn’t this amazing! Approximately 8 out of 10 women who undergo GAE will experience significant improvement even the 3 years after the procedure.
How does Dr. Nanavati (Interventional Radiologist (IR)) treat Knee Pain with the Genicular artery embolization procedure?
For a better understanding, let’s start with the concept. Knee pain/stiffness occurs from synovial inflammation(cell lining the knee joint). Inflammation thrives on extra blood supply. and additional blood supply promotes the growth of synovial membranes that release chemicals in the knee joint which in turn damages more tissue and results in more inflammation – pain – stiffness. This is a vicious cycle.
How do you break this cycle? The underlying principle is to cut off the blood supply (for oxygen and nutrients) via Genicular arteries. This results in less synovial growth- less chemical release in the knee joint – less inflammation – significant pain release – less stiffness – better growth – prevent further joint damage.
Under X-ray guidance and sedation, Dr. Nanavati accesses the artery in the leg/wrist/groin through a small incision, the size of a rice grain. Dr. Nanavati then guides a very thin catheter (about the size of a strand of spaghetti) into the incision and through your blood vessels to the Genicular arteries supplying blood to the bad synovium(inner lining of the knee joint). Once the catheter is in the proper position, Dr. Nanavati releases small particles (like tiny sands) at the targeted location to block the small vessels and deprive the inflamed synovium of nutrients. When embolization is completed, the catheter is removed, and pressure is applied to the small incision to allow it to heal.
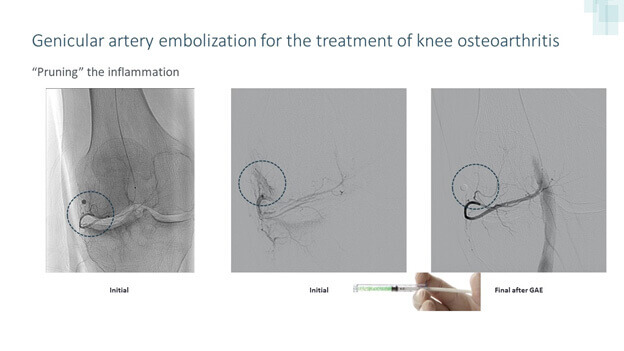
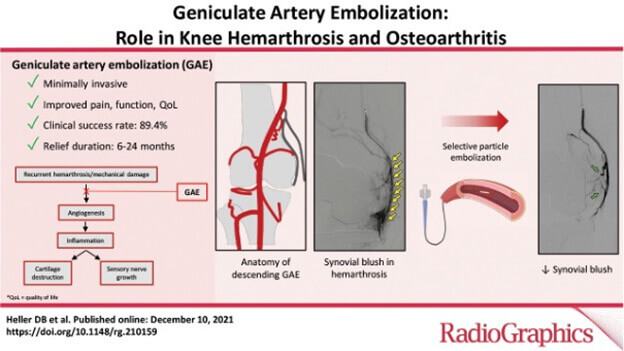
What happens when you Embolize Genicular arteries?
By cutting off the blood supply to an inflamed synovium, it disrupts the vicious cycle of inflammation – hypertrophy(overgrowth/over function) – Intraarticular(within knee joint) Chemical release – further destruction of the joint. This immediately pauses further joint inflammation-related knee arthritis(destruction) changes.
How long does it take to recover from Genicular artery embolization?
Can resume normal daily activities past 3 days of the GAE.
What are the side effects of Genicular artery embolization?
Minimal or No significant post-procedure problems. The most common issues were transient mild knee pain, self-limited numbness, and skin discoloration of the knee, as well as bruising at the puncture site. But most of the time “all symptoms resolved over time,”
What kind of follow-up care is typical after Genicular artery embolization?
Patient follow-ups are 2 weeks, 2 months, 6 months, and 1 & 3 years after the procedure.
How effective is Genicular artery embolization?
Judge yourself. We are more than happy to answer any questions or concerns in order to make an informed decision.
Baseline pain (visual analog scale [VAS] pain score) and symptom scores (Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index [WOMAC]) were assessed. This is compared at the follow-up to access clinical benefits in terms of symptomatic knee osteoarthritis (associated knee pain).
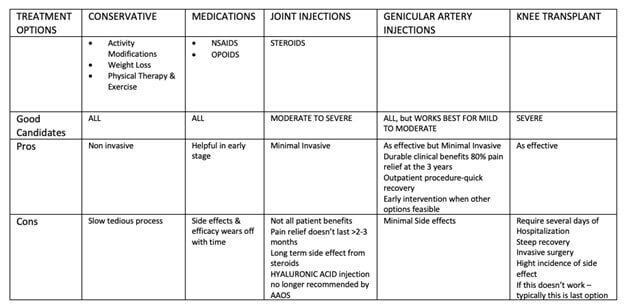
What is unique about Dr. Nanavati’s approach toward Knee pain? Am I a good candidate for Genicular artery embolization procedure?
Dr. Nanavati, an Interventional Radiologist, assesses, diagnose & evaluates every patient in a unique situation. Depending on the severity of the disease, Dr. Nanavati offers different management solutions.
Suppose you are suffering from persistent moderate to severe knee pain resistant to your ongoing conservative therapy, In that case, you may benefit from this novel minimal invasive GAE procedure (relieves knee pain without knee replacement surgery). Discuss your case with Dr. Nanavati & find out what is best treatment options suit you.
If you are willing to undergo knee replacement surgery for severe knee pain osteoarthritis or debilitating knee pain, & if you are interested in avoiding surgery & becoming symptoms-free, you may benefit from GAE.
Genicular artery embolization is such a superior treatment option, then how come I haven’t heard about the Genicular artery embolization procedure?
You are not alone. This is such a unique novel treatment that has not been popularised yet. Due to a lack of knowledge, Most of the patients either receive conservative therapy, physical therapy, or total Knee replacement surgery.